
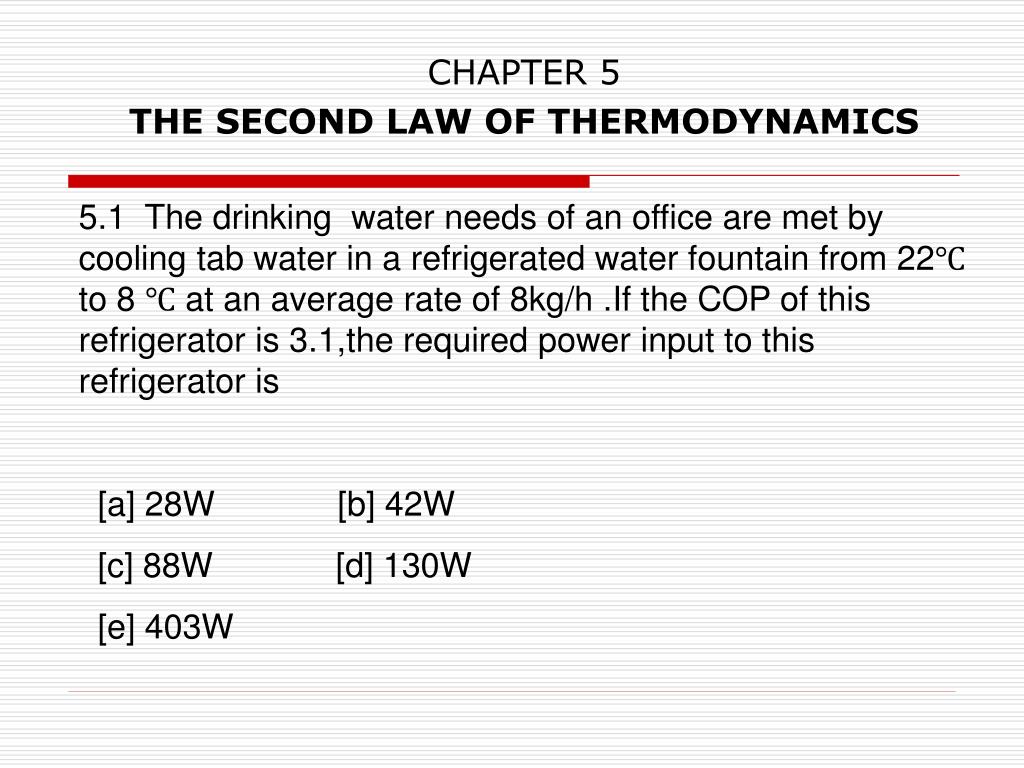
We ordinarily expect the temperature of a gas to decrease as it expands, and so we correctly suspect that heat transfer must occur from the surroundings to the gas to keep the temperature constant during an isothermal expansion. Carnot employed a reversible cycle to demonstrate the maximum convertibility. Now \(F=\text\) is a constant for an isothermal process. Example of the cyclic process: The Carnot cycle is the best example of the cyclic process which is explained below: The Carnot cycle: The cycle was first discovered by a French engineer Sadi Carnot in 1824 which works on reversible cycle and is known as Carnot cycle. See the symbols as shown in the figure above. From that, turning left on the shortest line keeps the heart away from anyone passing on the right hand side. Since pressure is constant, the work done is \(P\Delta V\). Everything is in the same order, but moved one position counter clockwise.
Life, Evolution, and the Second Law of Thermodynamics.Heat Death of the Universe: An Overdose of Entropy.Entropy and the Unavailability of Energy to Do Work.Which direction does a Ford engine turn It spins clockwise as you look at the front. work done on the system as the loop is traversed in a counterclockwise direction. That is, the actual crank bolt itself would be turned counterclockwise when facing the headlights from outside the car, in order to turn the engine/crankshaft clockwise. A system undergoing a Carnot cycle is called a Carnot heat engine.
#Engine cycle workdone counter clockwise driver
Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics 2) the engine rotation of clockwise is based on the driver being seated in the car.The most common engine cycle involves four strokes. The basic principle of operation is that a piston moves up and down in a cylinder, transmitting its motion through a connecting rod to the crankshaft which drives the ve hicle. The only catch is that running the fluid backwards through a pump isn’t the best way to make a turbine. 4.1 SPARK IGNITION ENGINES The operating cycle ofa conventional spark ignition engine is illustrated in Figure 4.1. Summarizing Applications of Thermodynamics The cycle moves counter-clockwise along the process path on a PV Diagram.Summarizing Carnot’s Perfect Heat Engine.Summarizing the Introduction to the Second Law of Thermodynamics.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
